A project is a temporary endeavor that involves a collaborative effort to create a new product, service, or other result as defined in the Project Vision Statement. Every project is affected by the constraints of time, cost, scope, quality, risks, benefits, resources, and other limitations. For a successful project delivery, it is important to choose an appropriate project management/delivery methodology or framework.
Scrum is one of the most popular Agile frameworks. It is an adaptive, iterative, fast, flexible, and effective framework designed to deliver significant value quickly and iteratively throughout a project. The Scrum framework consists of three areas: principles, aspects and processes.
Scrum processes address the specific activities and flow of a Scrum project from its initiation to closure. In total there are nineteen processes which are grouped into five phases. Scrum aspects refer to the aspects of the project that must be addressed and managed throughout a Scrum project’s lifecycle. Scrum principles are the core guidelines for applying the Scrum framework and should mandatorily be used in all Scrum projects.
The Scrum framework is driven by the goal of delivering maximum business value in a minimum time span. To achieve this practically, Scrum believes in Iterative Development of Deliverables. In most complex projects, the customer may not be able to define very concrete requirements or is not confident of what the end product may look like.
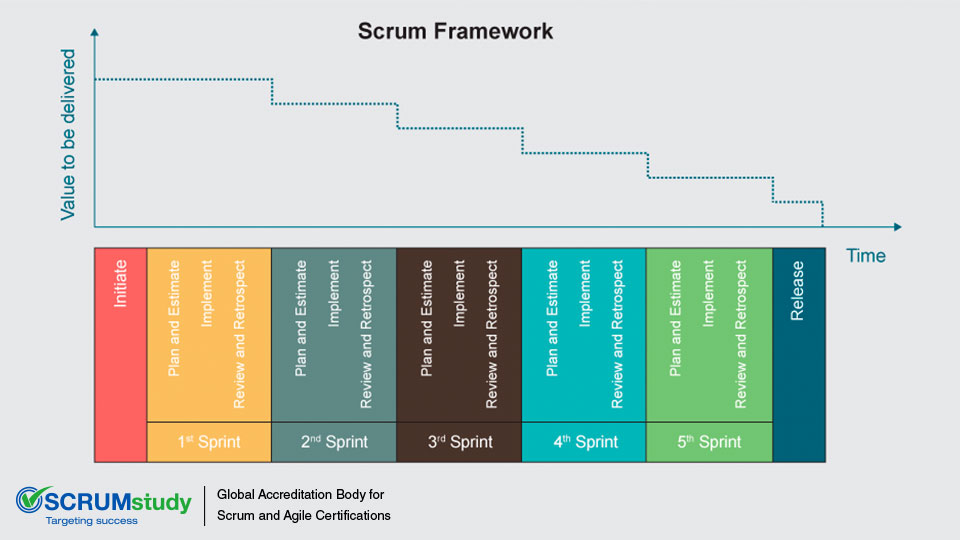
The iterative model is more flexible in ensuring that any change requested by the customer can be included as part of the project. Thus, the benefit of iterative development is that it allows for course correction as all the people involved get a better understanding of what needs to be delivered as part of the project and incorporate these learning in an iterative manner.
This ensures that the time and effort required to reach the final end point are greatly reduced and the team produces deliverables that are better suited to the final business environment.









