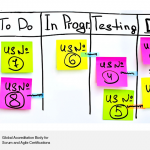
The Daily Scrum is one of the most important aspects of the Scrum framework. Scrum’s transparency comes from openly viewable information tools such as the Scrumboard, which shows the progress of the team. The team uses a Scrumboard to plan and track progress during each Sprint.
![Scrumboard-[Converted]](http://blog.scrumstudy.com/wp-content/uploads/Scrumboard-Converted.jpg)
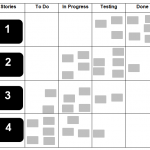
The Scrumboard usually contains four to five columns to indicate the progress of the estimated tasks for the Sprint:
- A ‘Stories’ column for the list of tasks (optional, usually a part of the Prioritized Product Backlog)
- A ‘To Do’ column for tasks not yet started
- An ‘In Progress’ column for the tasks started but not yet completed
- A ‘Testing’ column for tasks completed but in the process of being tested, and
- A ‘Done’ column for the tasks that have been completed and successfully tested.
At the beginning of a Sprint, all tasks for that Sprint are placed in the ‘To Do’ column and are subsequently moved forward according to their progress.
The Scrumboard should preferably be maintained manually on paper or a white board, but can also be maintained electronically in a spreadsheet.
The Scrum Team should change or add to the Scrumboard as required so that the board provides visual information and control about the work going on as agreed and committed by the team. Updating or referring to the Scrumboard during the Daily Scrum keeps the team focused on the tasks that remain and their priorities.
For interesting articles about Scrum and Agile, visit www.scrumstudy.com/blog