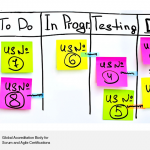
Scrum boards are an important and effective way to maintain transparency on Scrum projects. Scrum boards depict the progress of the team during a particular sprint. By using Scrum boards, all team members can concentrate on their tasks. Each task is represented by a card or post-it notes. A Scrum board contains four columns to indicate the progress of the estimated tasks for the Sprint:
‘To Do’ column – This column is for tasks not yet started and that need to be completed.
‘In Progress’ column – This column is for tasks that are started and are being on by a Scrum team member. Cards from the ‘To Do’ column are generally moved to this column during the Daily Stand-up meeting by the team member who intends to work on the task.
‘Testing’ column- This column is for tasks completed but in the process of being verified or tested.
‘Done’ column – All tasks that have been worked on and verified successfully will be listed in this column.
At the beginning of a Sprint, all task cards for that Sprint are placed in the ‘To Do’ column and are subsequently moved forward according to their progress.
Scrum boards are ideally placed in the centre of the collocated workspace so that every team member has easy access to it. The Scrum board should preferably be maintained manually on paper or a white board, however, when teams are distributed dedicated software or simple spreadsheets can be used as Scrum boards.
The Scrum Team should change or add to the Scrum board as required so that the Scrum board provides visual information and control about the work going on as agreed and committed by the team.
An example of a Scrum board- Image courtesy – ScrumBOK