Importance of Sprint Backlog in a Scrum Project
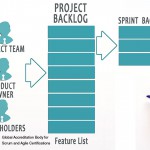
Let us begin with a discussion on what a Sprint Backlog. The Scrum Team creates the Sprint Backlog
and Sprint Burndown Chart using the User Stories and the Effort Estimated Task List during Sprint
Planning Meeting. During Sprint Planning Meeting, the User Stories, which are approved, estimated,
and committed during the Approve, Estimate, and Commit User Stories process, are taken up for
discussion by the Scrum Team. Each Scrum Team member also uses Effort Estimated Task List to
select the tasks they plan to work on in the Sprint, based on their skills and experience. The list of
the tasks to be executed by the Scrum Team in the upcoming Sprint is called the Sprint Backlog.
It is a common practice in Scrum that the Sprint Backlog is represented on a Scrumboard or task
board, which provides a constantly visible depiction of the status of the User Stories in the backlog.
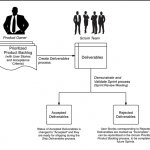
Also included in the Sprint Backlog are any risks associated with the various tasks. Any mitigating
activities to address the identified risks would also be included as tasks in the Sprint Backlog. Once
the Sprint Backlog is finalized and committed to by the Scrum Team, new user stories should not be
added – however, tasks that might have been missed or overlooked from the committed user stories
may need to be added. If new requirements arise during a Sprint, they will be added to the overall
Prioritized Product Backlog and included in a future Sprint.
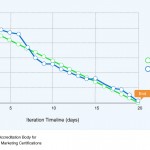
An important tool associated with the Sprint Backlog is the Sprint Burndown Chart. It is a graph that
depicts the amount of work remaining in the ongoing Sprint. The initial Sprint Burndown Chart is
accompanied by a planned burndown. The Sprint Burndown Chart should be updated at the end
of each day as work is completed. This chart shows the progress that has been made by the Scrum
Team and also allows for the detection of estimates that may have been incorrect. If the Sprint
Burndown Chart shows that the Scrum Team is not on track to finish the tasks in the Sprint on time,
the Scrum Master should identify any obstacles or impediments to successful completion, and try
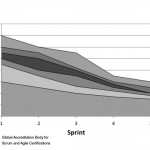
to remove them. A related chart is a Sprint Burnup Chart. Unlike the Sprint Burndown Chart which
shows the amount of work remaining, the Sprint Burnup Chart depicts the work completed as part of
the Sprint.
So, it can be said that Scrum professes minimum documentation and the Sprint Backlog fulfills
purposes of more than one project document and thus plays an important part in maintaining and
transferring project information.